Charging times of e-cars 2023
Before buying an electric car, it is advisable to find out about the charging power and duration of the vehicle. Because these factors determine the purpose for which it is suitable. The charging power indicates how quickly the battery of an electric car or a plug-in hybrid is charged. It is measured in kilowatts (kW).
Whether via a household socket, a wallbox or at a fast-charging station – the charging times of e-cars differ at these points. In addition to the charging time of an electric car, the capacity of the battery is also an important decision criterion. Manufacturers specify it in kilowatt hours (kWh) – the unit with which electricity providers bill energy costs.
This makes it easy to calculate what charging the electric car will cost. This way you can also calculate a large part of the maintenance costs for an e-car. Note: Due to charging losses, not as much electricity arrives in the car battery as the meter in the house indicates. Charging losses are completely normal, but should be taken into account for the advance payment, for example.
How long does an e-car take to charge?
In everyday life with an electric car, it is important, among other things, to know how long it will charge. To calculate the charging time of an electric car, you need the size of the battery and the charging power with which it is charged. With these two figures, the charging time of the electric car can be easily calculated. Theoretically, a battery with a capacity of 100 kWh can fully charge within an hour with a charging capacity of 100 kW.
It can be said that the lower the charging power, the more direct the relationship between it and the charging time. For example, an empty battery with a capacity of 23 kWh on a connection with 2.3 kW charging power will theoretically fully charge in ten hours. In practice, this usually looks different - because how quickly the battery charges depends on numerous factors.
Charging an electric car: How the duration is influenced
- Charging power of the charging station used
- Charging power of the onboard charger in the car
- Traction battery capacity
- Battery level in the car
- Battery temperature
- Battery Health – State of Health (SOH)
Charging options for e-cars and their performance
If you want to charge your electric car, you have various options. How much charging power can be achieved depends, among other things, on the power connection used.
Household socket
At a household socket, electricity usually flows at a maximum of 3.6 to 3.7 kW – often it is only 2.3 kW. The value results from the voltage (volts) and the current (amperes). Modern cables are usually fused with 16 amps. Multiplied by the voltage, the maximum charging power in watts results. If you divide this wattage by 1,000, you get the kilowatt value.
An example:
(230 volts x 16 amps) / 1,000 = 3.68 kW
In practice, however, this value is rarely reached. This is due to the fact that other consumers are connected to the line. If you want to charge safely at full power, you therefore need a separately fused line.
The charging process of the electric car nevertheless loads the house line at full power for many hours. This can generate great heat - and there is a risk of fire. To prevent this from happening, it is important to have the domestic power grid checked by an expert before you want to charge your e-car there permanently.
It is also important that the socket is permanently current resistant – normal household sockets usually do not meet this criterion. Furthermore, you should not hang an extension cord between the charger and the socket, as it can cause an electric shock. The reason: Most extension cords are not designed for that much power.
Wallbox
Wallboxes for electric cars are charging stations for the home. With them, you can charge safely and much faster than at the socket. Depending on the house installation, three phases can be interconnected. This makes charging capacities of around 11 kW (3 x 3.68 kW) possible. Another plus: The wall-mounted charging station communicates with the vehicle and queries the currently possible maximum power – this reduces the charging time of the electric car and protects the battery at the same time.
AC charging station
Alternating current (AC) comes from power lines. However, the traction battery of the electric car requires direct current (DC). Nevertheless, the majority of public charging stations only emit alternating current. For this purpose, e-cars have a so-called onboard charger. It converts the alternating current from the charging station into direct current. This results in charging losses.
Similar to domestic wallboxes, charging stations are usually connected to three phases. They can therefore also charge with an output of 11 kW – some even manage up to 22 kW. In the case of public charging stations, the available charging power is often distributed among several vehicles, which extends the charging time of the individual e-cars.

Charging station with direct current
If you are looking for short charging times for your e-car, you should seek out DC charging stations. The station converts the alternating current into direct current itself. This allows the energy to flow much faster into the battery. Charging stations at supermarkets and the like usually manage 50 kW. There are also models that charge at up to 150 kW. Tesla's latest generation Supercharger V3 even charges with up to 250 kW.
This value is topped by fast charging stations from Ionity. This is an association of various car manufacturers such as Audi and BWM, Ford and Mercedes as well as Porsche and VW. These stations charge with up to 350 kW: So far, however, there is no car that can accommodate this charging power. Whether via the integrated navigation system or an app, you can easily find a suitable charging station for your electric car.
How long does an e-car charge at different charging stations?
Depending on the type of charging option you use, the time it takes for the e-car to be fully charged differs. The theoretically achievable value is more realistic if the charging power is low. This is because batteries can only tolerate high charging capacities up to a certain fill level. The theoretical values listed in the table can only be achieved under optimal conditions.
| Types of charging option | Household socket | Wallbox | AC charging station | DC charging station |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Usual charging power | 2.3 to 3.6 kW | 3.6 to 11 kW | 11 to 22 kW | 50 to 350 kW |
| Charging time for 50 kWh | 14 to 22 h | 4.5 to 14 h | 4.5 to 2.3 h | 10 min to 1 h |
The charging power of electric cars
As with the charging station, the charging power of electric cars also differs. It varies depending on the model and depends on which onboard charger is installed. If he cannot convert the charging power, it is reduced – and it takes longer for the electric car to be charged.
Usually, electric cars can only tolerate 11 kW of alternating current – plug-in hybrids only 3.6 to 3.7 kW. Due to the smaller battery, it is not worth installing an expensive charger with high power. Therefore, very few PHEVs can be charged at DC charging stations, because the charging capacities are significantly higher there.
The charging capacities of e-cars vary greatly. At the lower end are models such as the Nissan Leaf, which charges with a maximum of just under 50 kW, or the Hyundai Ioniq Electric with a maximum charging power of 45 kW. Small cars such as the Opel Corsa-e and the Peugeot e-208 charge with up to 100 kW. An Audi e-Tron manages 150 kW, while the Porsche Taycan refuels with up to 270 kW of electricity. Only Tesla is similarly fast – the Model 3 now manages 250 kW. Other examples of electric cars and their maximum charging power with direct current in descending order:
| Car model | Charging power AC | Charging power DC | Battery size | Charging time minimal |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tesla Model 3 | 11 kW | 250 kW | 75 kWh | approx. 35 min (0 to 80 %) |
| Audi e-Tron 55 | 22 kW | 150 kW | 95 kWh | approx. 30 min (5 to 80 %) |
| Volkswagen ID.3 | 11 kW | 135 kW | 77 kWh | approx. 35 min (0 to 80 %) |
| Mercedes EQC | 7.4 kW | 110 kW | 80 kWh | approx. 40 min (10 to 80 %) |
| Kia e-Niro (204 hp) | 11kW | 80 kW | 68 kWh | approx. 54 min (0 to 80 %) |
| Hyundai Kona (204 hp) | 11kW | 77 kW | 67.5 kWh | approx. 54 min (0 to 80 %) |
| Renault Zoe | 22 kW | 50 kW | 50 kWh | approx. 60 min (0 to 80 %) |
| BMW i3 | 11 kW | 50 kW | 44.2 kWh | approx. 30 min (20 to 80 %) |
The more powerful the charging technology, the more expensive it is. For this reason, weaker onboard chargers are installed in cheaper electric cars with short ranges. The reason: e-car batteries with a smaller charging capacity fill up faster than larger ones. Low charging capacities are therefore easier to get over. In addition, high charging speeds stress the battery cells more than low ones. Therefore, even with cars with a high charging capacity, it is advisable to only use them when necessary.
In addition, you should never fully charge the e-car at the fast charger if possible. This is because it strains the battery and is not time-efficient. This is because the charging speeds decrease massively when the battery level goes to 100 percent. The result: The charging time of the electric car increases and thus also the electricity costs - many e-car drivers want to avoid this with rising electricity prices.
The battery level as a limiting factor
The charging times of electric cars increase the closer the battery level approaches the maximum fill level. Therefore, most manufacturers only specify the fast charging time up to a fill level of 80 percent. Because with a battery level of 80 percent or more, the possible charging power usually drops rapidly. There are reasons for this technical limitation: it protects the battery, reduces the load on the cells and thus extends their service life.
No electric car achieves the maximum possible charging power over the entire charging process. Many reach it only for a very short time. Some examples:
Tesla Model 3
The Model 3 achieves a maximum of 250 kW on the latest generation of Tesla Superchargers. However, a look at the charging curve shows that the maximum power is very short and only occurs when the battery charge level is very low. According to a study by the consulting firm P3 Automotive, the peak is reached at five percent charge level, already at 20 percent it is only a little more than 200 kW, at half around 125 kW, at 80 percent it is still 50 kW.
Porsche Taycan
The Taycan achieves an output of 250 kW at around five percent battery level – but can increase it to 270 kW by up to 45 percent. After that, it falls steadily until there is less than 150 kW at 80 percent.
Audi e-Tron
With a maximum of 150 kW, the e-Tron charges significantly slower than the models from Porsche or Tesla. However, it keeps the performance almost constant between ten percent battery level and just under 80 percent - only then does the charging power drop quickly.
In addition to the models from Tesla, Porsche and Audi, the following infographic also compares the Hyundai Kona and Kia E-Niro as well as the VW ID.3 and the BMW i3.
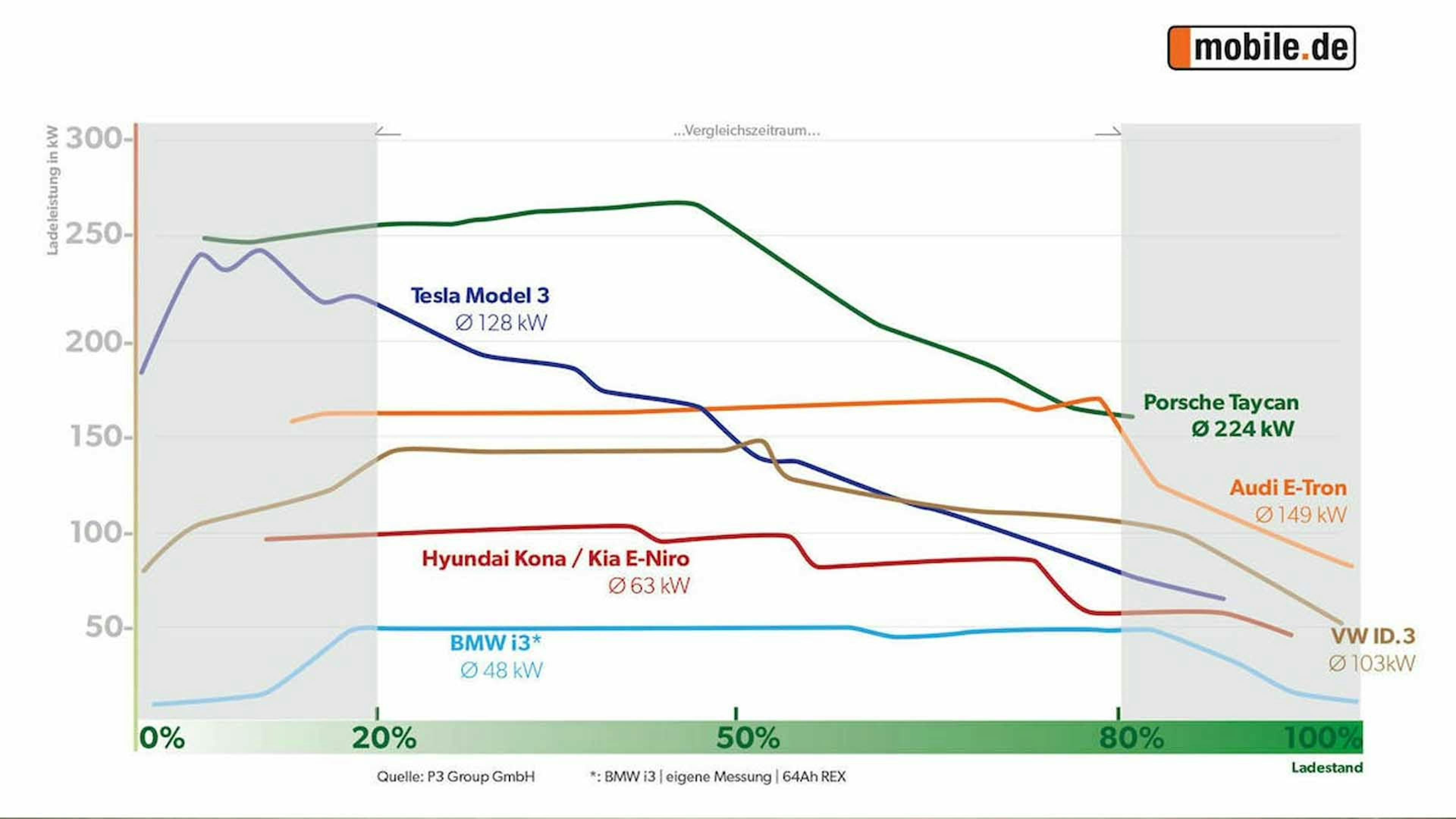
Based on the charging curves, P3 Automotive has determined the average charging power between 20 and 80 percent battery level. This "charging window" is relevant for experts in practice, as most drivers of electric cars charge the battery from 20 percent at the latest. In this way, they want to avoid lying down unexpectedly. From 80 percent, on the other hand, the charging power is technically throttled.
In this "ideal charging range" between 20 and 80 percent battery level, the Taycan achieves an average charging power of 223 kW, while Tesla's Model 3 only manages 128 kW. The Audi e-Tron reaches 149 kW – almost the maximum charging power.
The influence of environmental factors on charging performance
Anyone who expects to always charge with their Porsche Taycan with an average of 223 kW is mistaken. This is because environmental factors also influence the fastest achievable charging times for e-cars.
One of the most important is temperature. The chemistry in the battery cells reacts sensitively to cold and heat. Especially in winter, the maximum possible range drops drastically in some cases - and the charging time of the electric car is extended.
The chemistry in an electric car battery works best between about 20 and 30 degrees Celsius. At these temperatures, the longest ranges, the highest charging capacities and the shortest charging times can be achieved. E-car manufacturers are therefore trying to ensure the optimal climate with special temperature management – both when driving and charging. How well this succeeds has a direct influence on the charging time.

In addition to the outside temperature, the driving style also has an influence on the system temperature. If you drive fast, constantly accelerate hard and brake hard, you put a strain on the system. If the car comes to the charging station "hot", the charging power is initially low. The same applies when it is on the road at night in sub-zero temperatures and is being charged.
In both cases, good temperature management can optimize charging performance. However, energy must be used for this. In this case, it comes from the charging station. This in turn can extend the charging time of the e-car to a small extent and increase costs.
Conclusion: Reach your destination quickly with high charging power?
There are many factors that influence the duration of e-car charging. One thing is clear: If you plan to drive long distances more often with an electric car, you should not only look at the range - the charging power plays at least as important a role. Because every minute saved at the charging stop gets you to your destination earlier. However, the highest charging power is of little use if the electric car drains the battery just as quickly.
Find the right electric car with these search filters on mobile.de
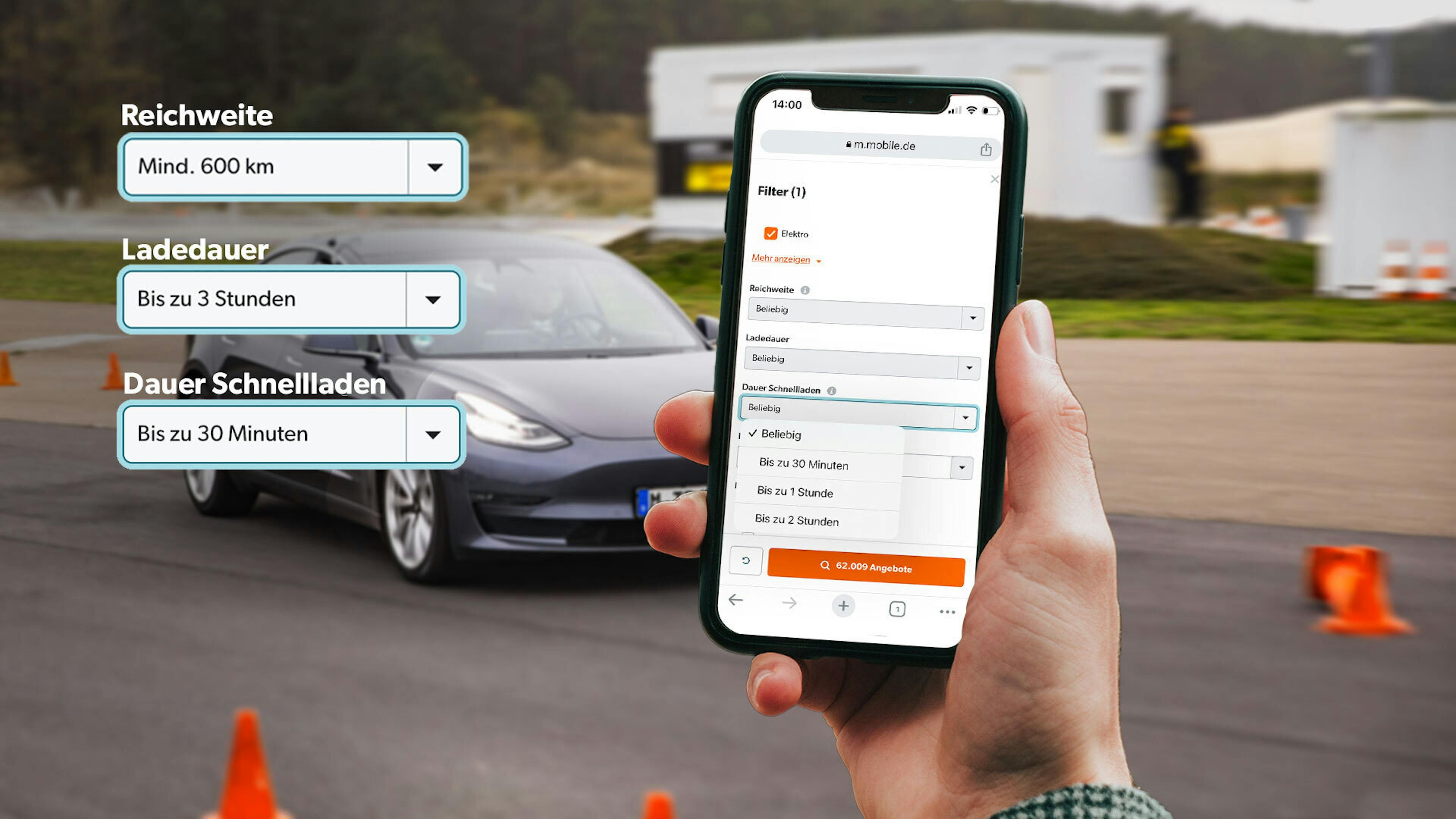
On mobile.de, there are new filter options that make it easier for you to find the right electric car. If you select "Electric" as the fuel type in the other filters of the desktop version of the portal, a new submenu with additional tabs will pop up. When searching for your desired electric car, you can now set the desired minimum range, as well as limit the charging time at conventional charging points and fast charging stations. On the advertisement page of the respective vehicles, the plug type is now also displayed.
You can also specify how large the battery capacity of the electric car should be. Since some manufacturers rent or lease the batteries of their e-cars separately from the actual vehicle, you can choose whether the battery should be included in the purchase or whether you want to rent it. You can also set that you are looking for a car without a battery.
